Using base-level field permissions to control editing in interfaces
You have a medium-sized team of around 50 people that has recently moved to a newly built interface. Everyone in this team will have editor permissions for all the fields they see in the interface pages.
You also want to be transparent with your entire organization of around 300 people and share this interface with them. Many will be making requests via a form that creates records in the interface. You would like to restrict them to editing only a few fields.
Is this possible? Or will you have to limit them to having commenter permissions only?
Understanding the permission layers
You can set permissions at both the interface layer and the data layer.
At the interface layer, you can control whether a field is editable or view-only for everyone who has access to that interface. This is an all-or-nothing setting. You cannot make a field editable for some people and view-only for others at the interface level.
At the data layer, on the other hand, you can control which specific users or groups can edit which fields. This is where you restrict editing permissions to certain people.
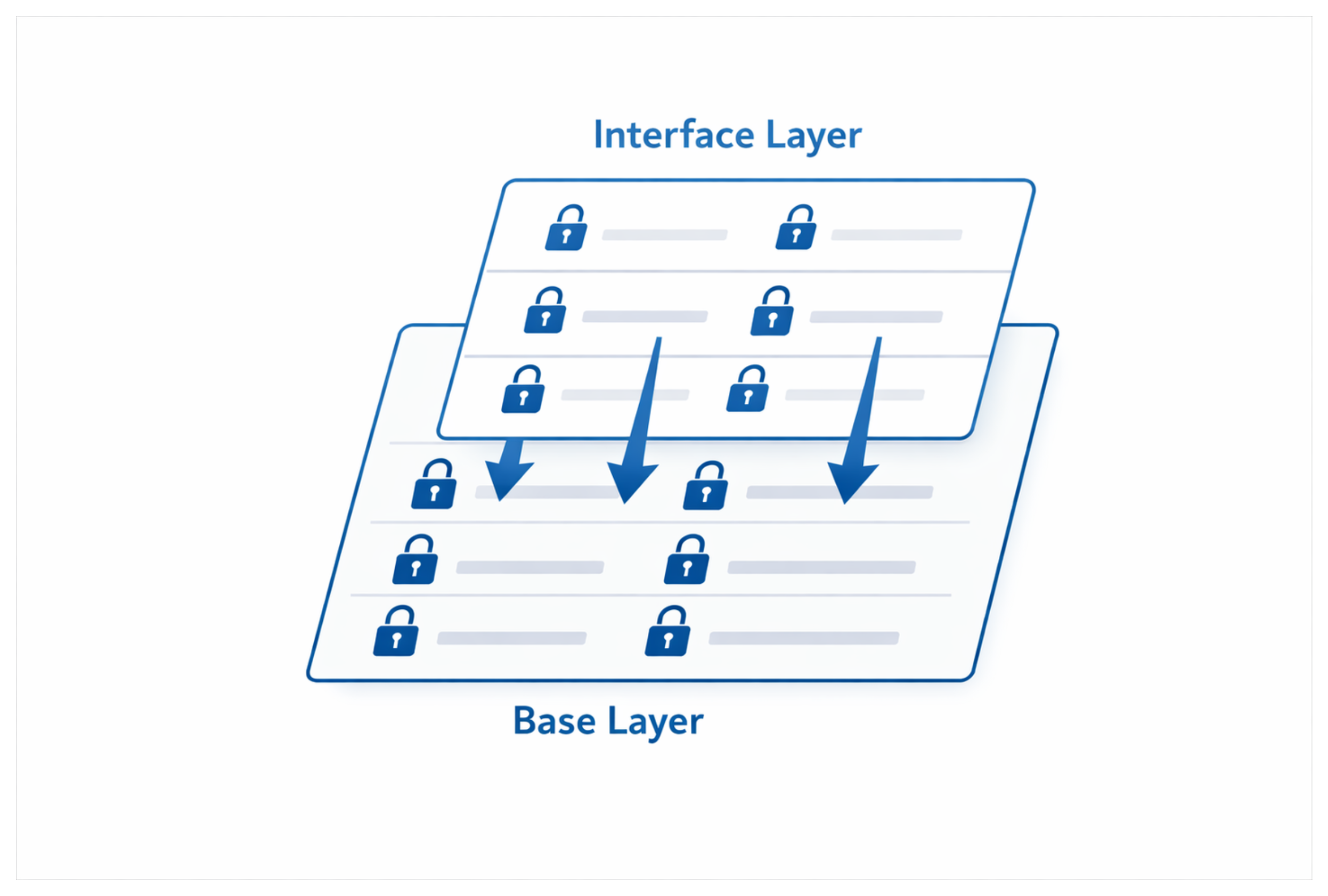
The base-level permissions will override the interface-level permissions. If someone does not have permission to edit a field at the base level, they will not be able to edit it in the interface, even if the field is set as editable in the interface settings.
This is how you can restrict people to editing only certain fields even when they have editor access.
Set up interface permissions
Give editor access to everyone who needs to use the interface. This includes both your core team of 50 people and the broader organization of 300 people.
At this point, everyone with editor access can technically edit any field they see in the interface. The next step restricts this at the data level.
Control editing through field permissions
Go into your base settings and configure field permissions for each field.
For fields that only your core team should edit, restrict editing permissions to just those 50 people. You can do this by individually specifying which users can edit each field.
For fields that everyone should be able to edit, such as form submission fields, leave the permissions as they are.
How this works in practice
Someone from your broader organization opens the interface and sees all the fields.
They can see all the other fields, but they will not be able to edit them since your base field permissions do not give them editor access.
Your core team opens the same interface. They can edit everything because they have both editor access to the interface and field-level permissions to modify all fields in the base.
This approach maintains transparency across your organization while controlling who can modify which data. Everyone sees the same interface, but editing capabilities differ based on field permissions set at the base level.